Recently, a paper titled Surface water and groundwater interactions in salt marshes and their impact on plant ecology and coastal biogeochemistry, written by Xin Pei (a professor at Hohai University) and 11 coauthors, was published in Reviews of Geophysics. This review paper covers the current state of knowledge on surface water and groundwater interactions in salt marshes and their impacts on ecology and the environment.
Salt marshes are highly productive intertidal wetlands providing important ecological services for maintaining coastal biodiversity, buffering against oceanic storms, and acting as efficient carbon sinks. However, about half of these wetlands have been lost globally due to human activities and climate change. Inundated periodically by tidal water, salt marshes are subjected to strong surface water and groundwater interactions, which affect marsh plant growth and biogeochemical exchange with coastal water. In this paper, a global analysis is provided to understand the distribution, hydrological and ecological functions, status and potential challenges of salt marshes. Surface water and groundwater interactions under different driving forces and factors are discussed and linked to soil conditions and biogeochemical processes. Current approaches including field measurements, radionuclide analyses and numerical modeling provide a guide for applications targeted at specific questions in salt marsh science and management. Knowledge gaps identified by this review suggest needs for further investigations into the complex and dynamic surface water and groundwater interactions and associated biogeochemical processes that characterize salt marshes. The paper provides guidance for the research and management of coastal wetlands.
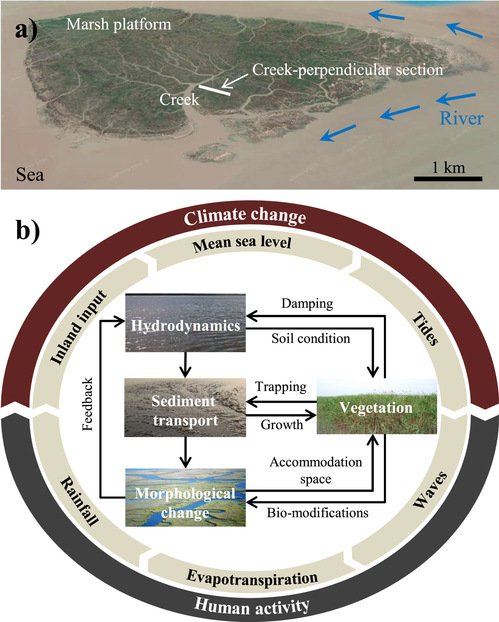
A typical bio-morphodynamic loop considering biophysical processes in salt marshes
This research is a joint effort of many international scholars from University of South Carolina, East China Normal University, Washington State University, University of Gothenburg, Southern Cross University, Westlake University and Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Key project, Research on the Evolution Mechanism and Ecological Restoration Methods of Wetlands in the Yangtze Estuary) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Jiangsu Excellent Youth Foundation, Coastal Hydrodynamics and Eco-geomorphology).
Reviews of Geophysics is an invitation-only reviews journal that provides overviews of recent research in all areas of the Earth and space sciences. The impact factor is 22 based on 2020 Journal Citation Reports.


